What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting (IF), is the most followed eating habit where an individual eats and fasts at distinct intervals. Unlike a diet which primarily includes the content of the meals, intermittent fasting considers the timing of the meals. This was primarily adopted due to perceived benefits to health of the individuals and the applicability of it on different individuals.
How Intermittent Fasting Works
Intermittent fasting for the most part has different periods which fit the individual’s lifestyle best. By incorporating fasting periods, the body changes gears in terms of energy and starts using fat instead of glucose within the red blood cells. Such transitions in metabolism help in recovering from multiple diseases.
Also Read: Low Glycemic Index Foods to Include in Your Diet (+ Weekly Meal Plan)
Types of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting schedules can be divided into several areas each concentrating on a certain range of availability:
16:8 Method
There are three meals and a further 8 hours for feeding as the last. This method is ideal for beginners as it allows a large eating window.
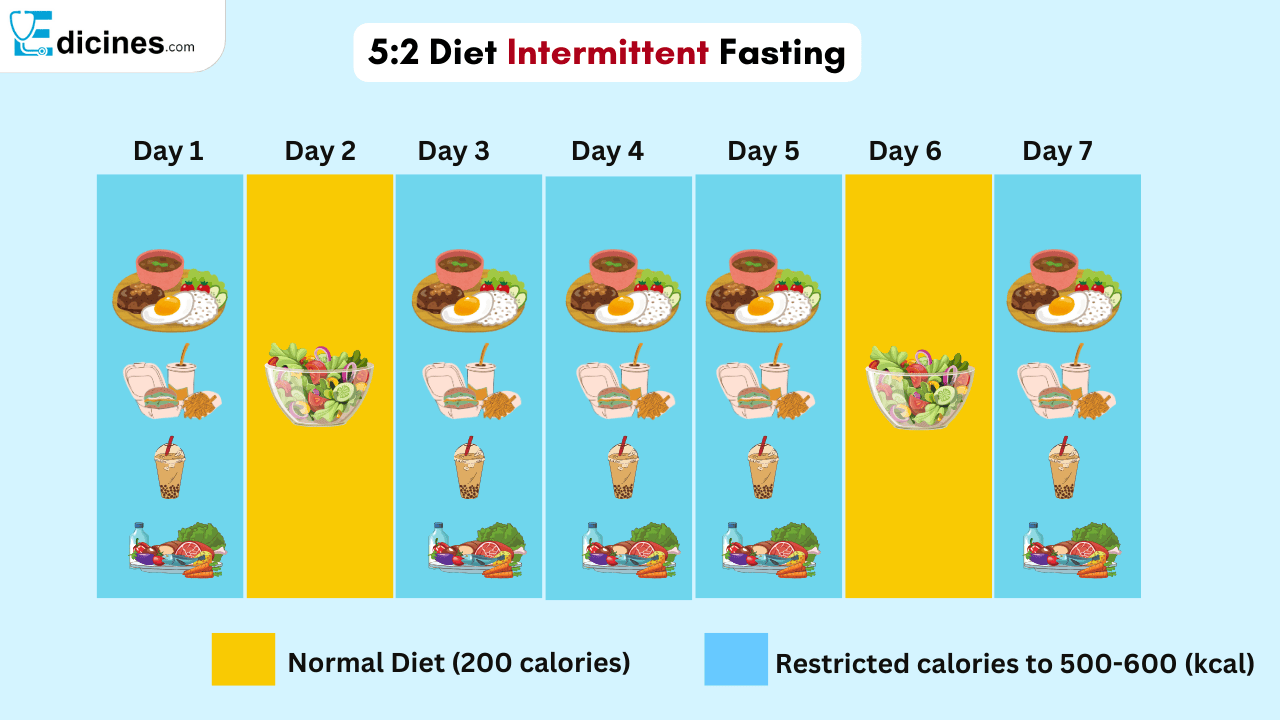
5:2 Method
Restrict calorie intake to about 500 or 600 on 2 days then eat normally for the rest allowing about 5 days a week. This approach allows for flexibility and less strict adherence.
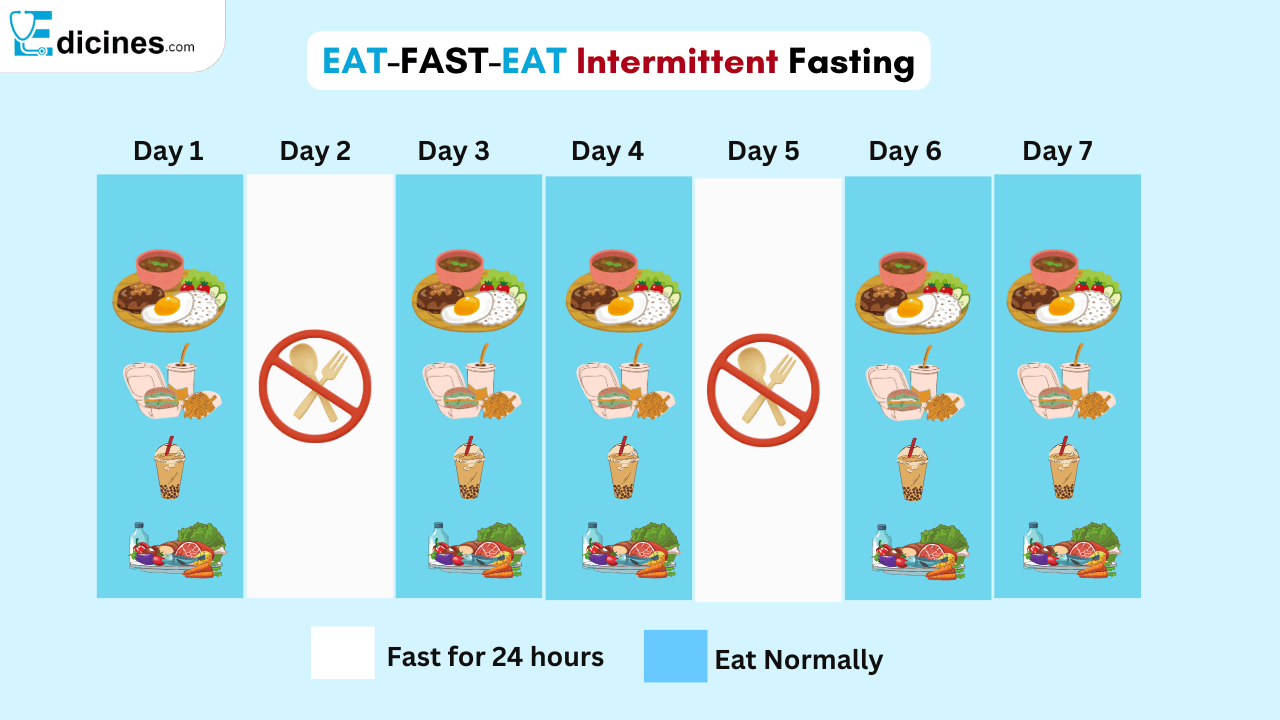
Eat-Stop-Eat
It usually involves fasting for 24 hours for two or even one day a week. This method is for people who fast regularly and can withstand long fasting periods.
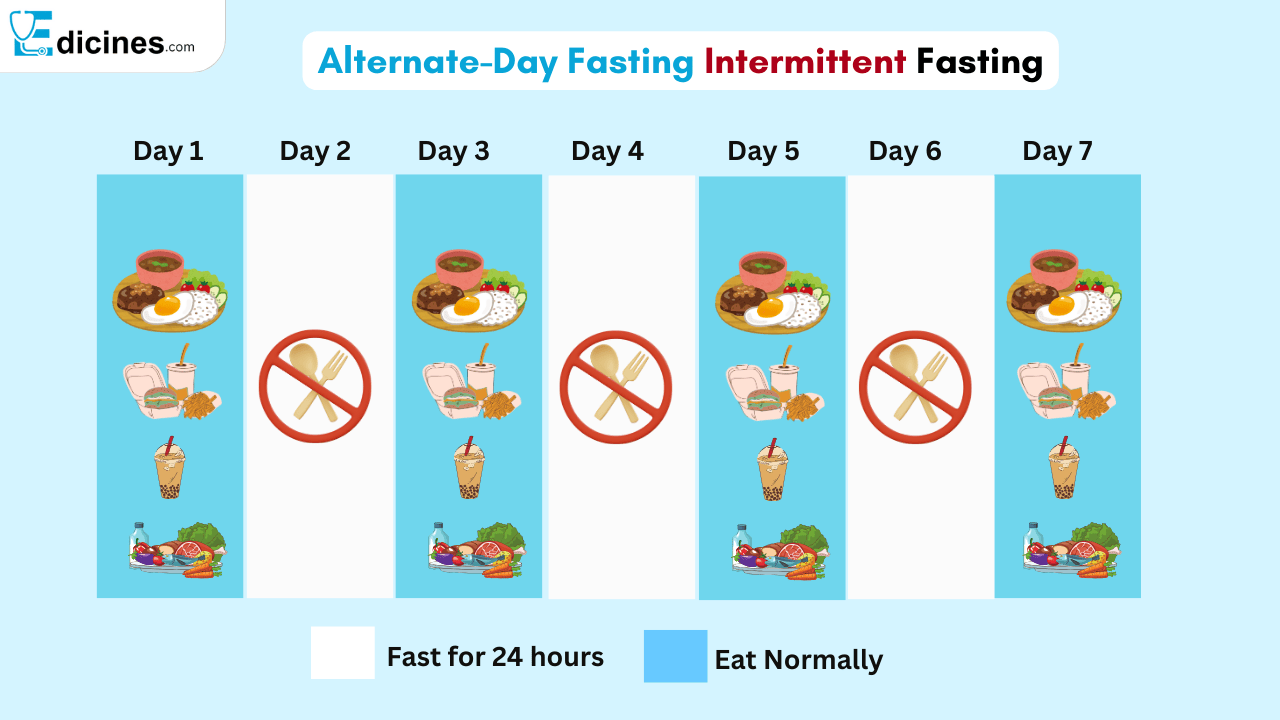
Alternate-Day Fasting
Cycle of eat days and fasting days. This could be difficult for starters but would work well with people who are used to fasting.
OMAD (One Meal A Day)
All the daily calories will be consumed in one meal. This method requires proper preparations and is suitable for practiced individuals.
Also Read: The Best Foods for Diabetics: A Balanced Diet Guide
How Intermittent Fasting Works
Intermittent fasting induces several metabolic processes that are advantageous such as improving health and increasing fat burning:
Fat Burning
The stored fat gets released in free fatty acid form, which is then used by the body for energy due to fasting.
Insulin Sensitivity
As one is fasting, insulin levels go down which in turn improves insulin sensitivity during eating thus reducing the risks of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Autophagy
Fasting achieves proper autophagy which is a repair process of the cells whereby damaged ones are degraded and renewed thus promoting long life and good health.
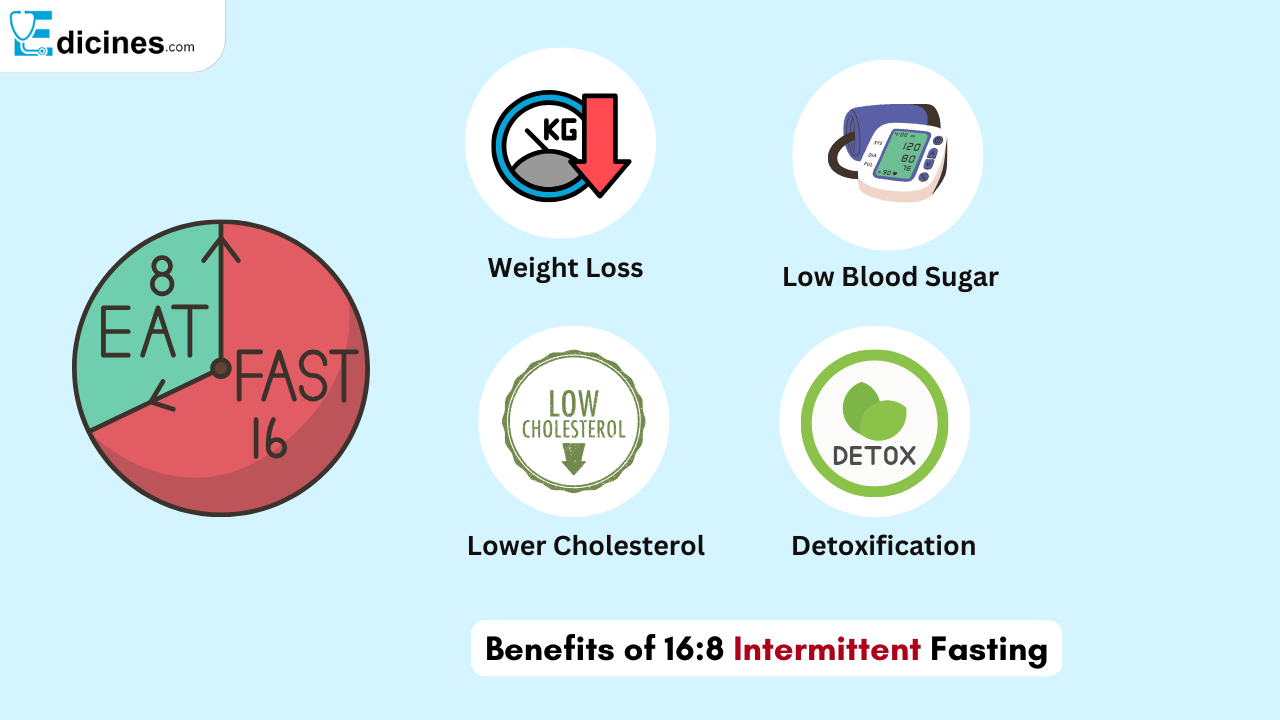
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
The advantages of intermittent fasting in relation to health are quite many and well established:
Weight Reduction and Loss
Intermittent fasting is a good practice for many if not all who would like to lose weight since it reduces calorie intake without people realizing and increases metabolism.
Improved Metabolic Health
There is also an improvement in many health factors in IF people such as low blood sugar, normal and regulated Cholesterols.
Better Insulin Sensitivity
This approach assists on cutting back the insulin resistance and consequently lowering the chances of Type 2 diabetes.
Potential Cardiovascular Benefits
Evidence, mostly from animal models, also suggest that intermittent fasting decreases the levels of blood pressure, cholesterol and triglycerides.
Mental Clarity and Focus
Concentration and brain performance on most people tends to improve after fasting.
Anti-Aging Effects
The anti-ageing effects of this process are thought to result from better cellular restoration and degeneration.
Risks and Side Effects of Intermittent Fasting
Although intermittent fasting has numerous upsides, there are groups of people who will not benefit from it as they experience negative effects such as:
Fatigue and Irritability
The first days of fast may make people suffer from tiredness and irritability due to the body adapting.
Headaches and Dehydration
Insufficient food and hydration during fasting can result in headaches and dehydration.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Prolonged fasting without attention to nutritional intake can lead to deficiencies over time.
Muscle Loss
Inadequate protein intake during eating periods may result in muscle loss if not properly managed.
Who Should Avoid Intermittent Fasting?
Avoid Intermittent Fasting Depriving Patients With Chronic Disease
Intermittent fasting has some recommended guidelines and some people need to steer clear of such regimes, such as:
Patients With Anorexia Or Other Eating Disorders
Pro fasting encourages some of these patients to binge on unhealthy and far too many foods and it should be avoided in such cases of anorexia.
People Having Chronic Ailments
One with diabetes or another chronic disease sine qua non, consult a health care provider before commencing intermittent fasting.
Women Who Are Pregnant Or Women Who Are Lactating
Nutritional needs are more intense in these stages and therefore fasting might do more harm than good.
Kids and young people
Because they are growing and their bodies develop, kids and young people are not advised to practice intermittent fasting.
Older members of society
Elderly people sometimes have their specific reasons not to fast due to health issues concerning their age.
Also Read: Beginner’s Guide to Strength Training at Home
Best Practices for Safe Intermittent fasting
Intermittent Fasting Strategies
Several measures whenever It comes to practicing intermittent fasting safes and effectively should be considered include;
Start Slowly Spears Fasting
Extreme lengths of fasting should be avoided and in order to reduce the actual fasting days period, the fasted phase can be fasted innocuously extended at times northwards over five or more days.
Increase Water Intake
Intake of extra water may be required, especially during fasting days, so as to maintain good health even during fasts.
Eat Balanced Meals Whenever Possible
While fasting is encouraged from time to time, there should be stress on a healthy balanced diet within the eating periods.
Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to hunger signals and be flexible with fasting durations based on how you feel.
Also Read: Weight Management Supplements: What You Need to Know
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the fasting duration for intermittent fasting?
A: fasting periods depend on the selected protocol. For instance, 16:8 protocol involves 16 hours of fasting and eating meals in 8 hours, while 5:2 protocol has reduced caloric intake for two days within a week that do not follow each other.
Q2: Is water allowed while intermittent fasting?
A: Of course, you can. It is important to drink enough fluids. During fasting periods, water, herbal teas, and black coffee are allowed.
Q3: Can intermittent fasting contribute to my weight loss goals?
A: Yes, intermittent fasting for weight loss may be effective since one eats fewer calories and burns fat more effectively.
Q4: Can women use intermittent fasting?
A: Normally, women can practice intermittent fasting, however, it is advisable to consider their hormones and reach out to a specialist in case of doubts.
Q5: Is it possible to train while on intermittent fasting?
A: Yes, most people do not change their fasting or training routines when fasting. Nevertheless, it may be advisable to schedule training sessions within the eating periods in order to enhance performance.
Q6: Are there any effects of intermittent fasting on muscle mass?
A: Adequate protein should be consumed at all times or else muscle mass may be lost. Strength training whilst practicing intermittent fasting may assist in preventing muscle loss.
Q7: What should come first, food and water or drinks, after siesta?
A: Whenever you would fast and later enter ketosis level, this fast should be broken with proper meals containing proteins, healthy fats, complex carbohydrates in order to avoid any form of recovery.
Conclusion
There are many benefits of following an intermittent diet such as weight loss, improvement in metabolic performance, and elevation of mental well-being. Nevertheless, it is necessary to understand the possible dangers and adverse effects of this mode of eating. A medical representative should be seen before embarking on any new eating practice.
Also Read: Best Cardio Exercises for Weight Loss: Lose Weight Quickly













