Did you know that it was reported that anxiety disorders are the world’s most common disorder and have affected 301 million people in 2019? The problem of anxiety and depression is becoming more and more serious and it is important to address these issues.
Understanding the symptoms of anxiety and depression is important for your mental health and will also help in better health management. This article will help you understand the symptoms, causes, and treatment of anxiety and depression.
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a feeling of fear, nervousness, tension, or unease that arises as a reaction to situations with uncertain outcomes or threats.
Definition and types
If a person experiences anxiety attacks frequently then they have anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorder is a mental health condition in which people often feel uncontrollable fear, nervousness, or unease in response to certain situations.
Feeling anxious when dealing with problems or situations with uncertainty can be normal but anxiety disorders are more serious.
There are different types of anxiety disorders. They are as follows:
- Generalized anxiety disorder: In this type of anxiety disorder, people feel excessive worry and fear about everyday things.
- Panic disorder: In panic disorder people get sudden panic attacks. Symptoms of panic disorder are fast breathing, chest pain, shaking, sweating, and chills.
- Social anxiety disorder: Social anxiety disorder is the feeling of intense fear in response to social situations. Its symptoms include feeling nauseous and heart racing in social situations, sweating, shaking, and inability to make eye contact.
- Specific phobias: Phobia is a feeling of intense fear or anxiety in response to certain situations or objects. The most common phobias are acrophobia, aquaphobia, astraphobia, aerophobia, etc.
Symptoms of anxiety
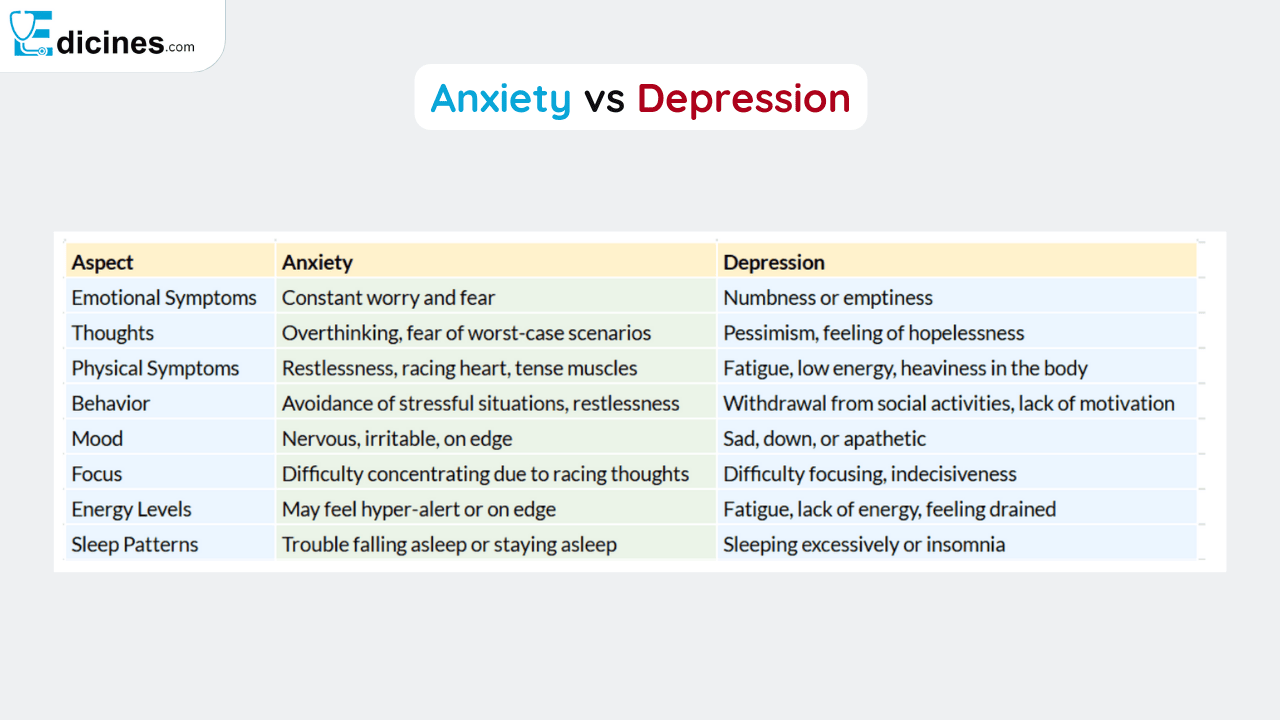
Due to anxiety, people might observe various physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. Some of these anxiety symptoms are
- Physical symptoms: rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, nausea, abdominal distress, insomnia, etc.
- Emotional and psychological symptoms: excessive worry, irritability, restlessness, etc.
- Behavioral symptoms: avoidance of certain situations, compulsive behaviors, etc.
Causes of anxiety
It is common to have anxiety but some people are more likely to develop anxiety disorder. This can be due to various factors. The main causes of anxiety are:
- Genetic factors and family history: family members with anxiety disorder history, parenting.
- Environmental factors: stress, trauma, life changes, abuse, severe losses.
- Neurobiological factors: brain chemistry and function
What is depression?
Definition and types
Depression, also known as depressive disorder, is a prevalent mental illness that causes a persistently low mood, loss of enjoyment, or disinterest in activities.
Common types of depressive disorders:
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Major depressive disorder also known as clinical depression causes consistently low or sad mood and a loss of interest in once-enjoyed activities.
- Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD): Persistent depressive disorder is a persistent feeling of depression that causes people to feel sad and empty on most days.
- Bipolar disorder: Bipolar disorder is a mental condition that causes sudden changes in a person’s mood.
Symptoms of depression:
Every person faces slightly different depression symptoms depending upon the type of depressive disorder but some of the common symptoms are
- Emotional symptoms: persistent sadness, loss of interest or pleasure, feelings of worthlessness or helplessness, frustration, irritability, etc.
- Physical symptoms: fatigue, changes in appetite or weight, sleep disturbances, chest pain, digestive problems, and headaches.
- Cognitive symptoms: difficulty in concentrating, indecisiveness, suicidal thoughts.
Causes of depression
Depression is a common mental illness and can be caused due to various factors. The common causes of depression are
- Genetic predisposition and family history
- Environmental factors: stressful life events, trauma, substance abuse
- Neurobiological factors: brain chemistry, hormonal imbalances
Diagnosing anxiety and depression
If a person faces anxiety and depression continuously, it is better to consult a doctor and get it diagnosed to avoid any serious problems.
How anxiety and depression are diagnosed
To diagnose mental health problems like anxiety and depression, mental health professionals use tools like DSM-5 and ICD-10. DSM-5 known as the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is a manual published by American Psychiatric Association (APA). Based on a predetermined set of criteria, including behavioral or emotional patterns and the length of time these patterns persist, the DSM-5 classifies 298 mental disorders.
ICD-10- the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) system is used to categorize and code all diagnoses and symptoms.
Other than these, there are common assessment tools like questionnaires, interviews, and psychological evaluations. This helps understand the mental health history.
Depression and anxiety are very common mental disorders and can adversely affect physical and mental health if not managed properly. Therefore, accurately diagnosing them is crucial.
Treatment options for anxiety and depression
People having anxiety or depressive disorder may not be able to manage it themselves. Therefore, there are many treatment options for anxiety and depression
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a treatment that involves a psychologist working on identifying unhealthy emotions, thoughts, and behaviors of a person by talking with them. There are several types of psychotherapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy, and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT).
Mental health professionals choose the type of therapy based on the person’s condition. Therapies help people manage various issues. It first identifies the core problem and then works on developing strategies to cope with it. It provides people with a safe and non-judgmental environment, which makes sharing problems easier.
Medications
Along with therapy, mental healthcare providers also prescribe medications. Some commonly prescribed medications for anxiety and depression are Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), Serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), anxiolytics, and mood stabilizers.
SSRIs help increase the level of serotonin in the brain. On the other hand, SNRI also increases the levels of serotonin and another molecule called noradrenaline or norepinephrine by blocking them from being reabsorbed.
Though these medications can help manage the symptoms they also have side effects. To choose the correct medications, it is important to consult mental healthcare providers.
Lifestyle changes and self-care
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle always results in good mental health. And so to fight against anxiety and depression, it is important to bring lifestyle changes that help cope with stress, anxiety, and depression. Some of these can be daily exercising, healthy eating, and having good sleep. For stress management, try mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and meditation.
It is not easy to manage mental health alone and therefore seeking family or social support can help.
Alternative therapies
Other than the treatments mentioned earlier, people also try alternative therapies like acupuncture, herbal supplements, and yoga.
Studies show that these therapies can help control anxiety and depression to some extent and they don’t have any major side effects.
Coping strategies and managing symptoms
Daily coping strategies
Medications and therapies alone can’t help if the person is not willing to bring the changes. Putting in efforts like lifestyle changes, self-care, avoiding alcohol and smoking, and overcoming fears and insecurities will help in coping with anxiety and depression.
For daily management of depression, try focusing on building relationships with friends and family, trying to understand your feelings, taking mindful walks, etc. Maintain a routine, set realistic goals, and practice self-compassion. This will help improve mental health.
When to seek professional help
If a person frequently experiences symptoms of anxiety and depression and it reaches a point where the person is not able to do daily activities then it is better to seek professional help. If you are facing problems finding a mental health care provider, you can consult your family doctor, friends, and family for references. Or you can get in touch with a local or national mental health organization.
Once you start getting treatment, you along with your therapist will be able to identify the problems and start working on managing the symptoms.
Resources and support
Online resources
It is important to be knowledgeable about your mental health, and online websites and apps can help you with it. Mental health resources like websites and apps help you understand the problems, their solutions, and the need for healthcare providers.
Knowing the helplines and crisis support services would be beneficial for people with anxiety and depressive disorder.
Support groups and communities
Managing anxiety and depression alone can be overwhelming. In this case, joining support groups for mental health can help. You get company and support from people going through the same problems.
Your physician or a medical facility, and websites of the National Institutes of Health for particular illnesses and ailments can help you find local or online support groups.
Conclusion
Anxiety and depression are the most common mental health conditions having symptoms like sweating, nausea, restlessness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, etc. They can be caused due to various reasons such as stress, trauma, severe losses, abuse, hormonal imbalances, and family history. And they can be treated with several therapies and medications.
But what is important is that you don’t ignore the signs of anxiety or depression. And if anyone you know is struggling with anxiety or depression, then reach out for support. Also, explore the available resources for better management of mental health.













